Cartesian control Tutorial: The Hula-Hoop motion¶
NAOqi Motion - Overview | API | Tutorial
Introduction¶
This tutorial explains how to use Cartesian control API to make the robot perform a Hula-Hoop motion (Torso control in position and in rotation).
Note
The tutorial is written in Python.
Download¶
You can download the Hula Hoop example here: almotion_hulaHoop.py
Please refer to the section: Python SDK Install Guide for any troubleshooting linked to python.
Code review¶
In this section we describe each important piece of code of the example.
NAOqi tools¶
- First, we import some external libraries:
- argparse: toolbox useful to define parameter
- motion: some useful definitions such as FRAME.
- almath: an optimized mathematic toolbox for robotics. For further details, see: libalmath API reference.
- ALProxy: create proxy to motion and robotposture modules
Then, the proxy to ALMotion module is created. This proxy is useful to call ALMotion API.
'''Motion: Hula Hoop'''
''' This example is only compatible with NAO '''
import argparse
import motion
import almath
from naoqi import ALProxy
def main(robotIP, PORT=9559):
'''
Example showing a Hula Hoop Motion
with the NAO cartesian control of torso
'''
motionProxy = ALProxy("ALMotion", robotIP, PORT)
postureProxy = ALProxy("ALRobotPosture", robotIP, PORT)
Initialization of the robot¶
When doing Cartesian control, it is important to be sure that the robot is in a good configuration. To
have the maximum range of control, the maximum stability and far away of singularity.
A PoseInit is a good posture before a Cartesian control
of the robot Torso.
# Wake up robot
motionProxy.wakeUp()
# Send robot to Stand Init
postureProxy.goToPosture("StandInit", 0.5)
Control point¶
Here, we specify that we want to control the Torso (see Effectors)
in the FRAME_ROBOT (see Frames) and that we want to control all the motion
with a AXIS_MASK_ALL (see Axis Masks).
We also specify that the torso path is defined in absolute.
effector = "Torso"
frame = motion.FRAME_ROBOT
axisMask = almath.AXIS_MASK_ALL
isAbsolute = True
useSensorValues = False
currentTf = almath.Transform(motionProxy.getTransform(effector, frame, useSensorValues))
Hula hoop motion¶
- We define the hula hoop motion with four checkPoints:
- forward / bend backward
- right / bend left
- backward / bend forward
- left / bend right
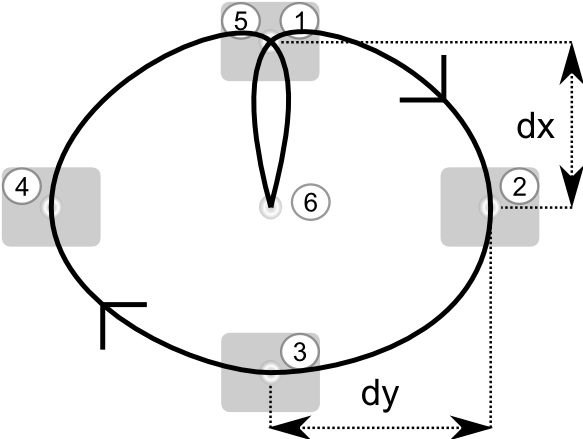
We define two loops of hula hoop. You can accelerate the motion by playing with the timeOneMove variable.
# Define the changes relative to the current position
dx = 0.03 # translation axis X (meter)
dy = 0.03 # translation axis Y (meter)
dwx = 8.0*almath.TO_RAD # rotation axis X (rad)
dwy = 8.0*almath.TO_RAD # rotation axis Y (rad)
# point 01 : forward / bend backward
target1Tf = almath.Transform(currentTf.r1_c4, currentTf.r2_c4, currentTf.r3_c4)
target1Tf *= almath.Transform(dx, 0.0, 0.0)
target1Tf *= almath.Transform().fromRotY(-dwy)
# point 02 : right / bend left
target2Tf = almath.Transform(currentTf.r1_c4, currentTf.r2_c4, currentTf.r3_c4)
target2Tf *= almath.Transform(0.0, -dy, 0.0)
target2Tf *= almath.Transform().fromRotX(-dwx)
# point 03 : backward / bend forward
target3Tf = almath.Transform(currentTf.r1_c4, currentTf.r2_c4, currentTf.r3_c4)
target3Tf *= almath.Transform(-dx, 0.0, 0.0)
target3Tf *= almath.Transform().fromRotY(dwy)
# point 04 : left / bend right
target4Tf = almath.Transform(currentTf.r1_c4, currentTf.r2_c4, currentTf.r3_c4)
target4Tf *= almath.Transform(0.0, dy, 0.0)
target4Tf *= almath.Transform().fromRotX(dwx)
path = []
path.append(list(target1Tf.toVector()))
path.append(list(target2Tf.toVector()))
path.append(list(target3Tf.toVector()))
path.append(list(target4Tf.toVector()))
path.append(list(target1Tf.toVector()))
path.append(list(target2Tf.toVector()))
path.append(list(target3Tf.toVector()))
path.append(list(target4Tf.toVector()))
path.append(list(target1Tf.toVector()))
path.append(list(currentTf.toVector()))
timeOneMove = 0.5 #seconds
times = []
for i in range(len(path)):
times.append((i+1)*timeOneMove)
Call the Cartesian control API¶
# call the cartesian control API
motionProxy.transformInterpolations(effector, frame, path, axisMask, times)
# Go to rest position
motionProxy.rest()